Schmitt Triggers have a wide range of applications in electronic circuits and are commonly used in applications such as signal processing, oscillators and timers. Understanding and mastering the effects and applications of Schmitt Triggers is important for electronics engineers. This article will take you through the definition, functions and application scenarios of Schmitt Triggers.
What is Schmitt Trigger
Schmitt Trigger is an electronic circuit commonly used in digital logic circuits and signal processing circuits. It has two different threshold voltage levels, and through these voltage levels, it can convert the input signal into a relatively stable output signal.
When the input signal exceeds the rising threshold, the output transitions from a low level to a high level. Conversely, when the input signal falls below the falling threshold, the output transitions from a high level to a low level. This dual-threshold structure enables the Schmitt Trigger to exhibit excellent robustness to input signals in high-noise environments, effectively suppressing noise present in the input signal.
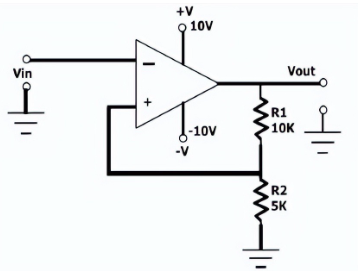
Schmidt trigger
Types of Schmitt Triggers
Schmitt Triggers are electronic circuits that provide hysteresis, which means they have two different threshold voltage levels for input signals. This hysteresis property helps in reducing noise and providing better noise immunity. There are different types of Schmitt Triggers based on their circuit configurations and applications. Some common types include:
Inverting Schmitt Trigger: This type of Schmitt Trigger has an inverting amplifier configuration. The output of the circuit is the inverse (complement) of the input signal. It switches states when the input voltage crosses different threshold levels.
Non-Inverting Schmitt Trigger: This type of Schmitt Trigger has a non-inverting amplifier configuration. The output of the circuit follows the input signal. It switches states when the input voltage crosses different threshold levels.
Schmitt Trigger Buffer: This type of Schmitt Trigger is used to provide buffering and amplification of signals while maintaining the Schmitt Trigger characteristics. It can be either inverting or non-inverting, depending on the configuration.
Op-Amp Schmitt Trigger: This type of Schmitt Trigger uses operational amplifiers (op-amps) to achieve the hysteresis effect. It provides precise control over the threshold levels and can be configured as an inverting or non-inverting Schmitt Trigger.
Schmitt Trigger with Hysteresis Adjustment: This type of Schmitt Trigger allows the adjustment of the threshold levels and hysteresis width using external resistors or potentiometers.
ALSO READ: What is Schmitt Trigger | How It Works
How Does a Schmitt Trigger Work
Schmitt Trigger utilizes positive feedback, it samples the output and feeds it back to the input to "strengthen" it, which is in complete contrast to negative feedback that attempts to counteract any changes to the output.
This enhancing property is useful, it allows the comparator to decide on the desired output state and keep it there, even within what is typically a dead zone. Take a look at this simple circuit: an inverting comparator with hysteresis.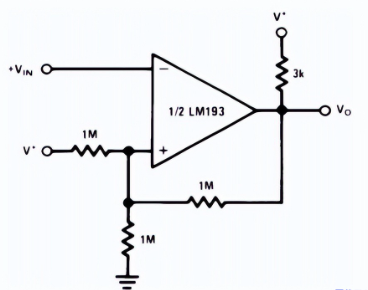
Inverting comparator with hysteresis
Assuming the input voltage is lower than the reference voltage at the inverting input, the output remains high.
V* represents the reference input voltage that creates a fixed bias at the non-inverting input. Since the output is pulled high through a pull-up resistor, it creates a current path through the feedback resistor, slightly increasing the reference voltage.
When the input exceeds the reference voltage, the output goes low. Typically, this doesn't affect the reference voltage in any way. However, due to the presence of the feedback resistor, the reference voltage will be slightly lower than the nominal value because the feedback and the lower reference resistor are now in parallel (as the low output shorts that terminal of the resistor to ground). With the decreased reference voltage, small variations in the input no longer cause multiple transitions - in other words, the dead zone no longer exists.
To make the output go high again, the input must now cross the new lower threshold. Once it crosses, the output goes high, and the circuit "resets" to its initial configuration. The input must only cross one threshold, resulting in a clean transition. The circuit now has two effective thresholds or states - it is bistable.
This can be summarized graphically.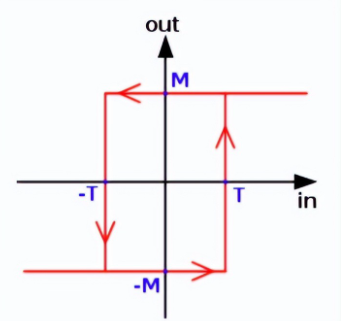
Phase lag curve
This can be understood in a general sense - the x-axis represents the input, and the y-axis represents the output. By tracing the line from x to y, we observe that once the threshold is crossed, the phase lag increases, and vice versa.
The operation is similar to that of an inverting comparator - the output again changes the configuration of the resistor network to alter the threshold and prevent unwanted oscillations or noise.
Why Schmitt Triggers
Schmitt Triggers have a memory function that allows them to generate stable output signals under specific conditions.
The main functions of Schmitt Triggers are as follows:
Stability: Schmitt Triggers can produce stable output signals even when the input signal undergoes transient changes, avoiding interference from the input signal.
Memory function: Schmitt Triggers can store the output signal and maintain a stable state of the output level under specific conditions.
Signal shaping: Schmitt Triggers can shape irregular input signals into regular input signals, improving the quality of the signal.
Schmitt Trigger vs Sensor
Schmitt Trigger is not a sensor itself, but Schmitt Trigger technology is used in some sensors such as temperature, sound, and light sensors to eliminate noise interference and improve signal accuracy. Additionally, Schmitt Triggers can be used in conjunction with sensors to control the operational state of the sensor based on the output signal of the trigger, or to expand the measurement range of the sensor, enhancing its functionality and applicability.
ALSO READ: Understanding the Crankshaft Position Sensor(Definition, Symptoms & Testing)
Schmitt Triggers applications
Digital signal filtering: Schmitt Triggers can strip away unnecessary signals mounted on the signal source, ensuring smooth operation of the equipment.
Transmission lines: In communication lines, noise signals may repeat several times or more, which can interfere with signal transmission. Using Schmitt Triggers can prevent interference caused by these repeated signals, enhancing the reliability and stability of signal transmission.
Modems: In digital modems, Schmitt Triggers can be used to maintain a consistent series of binary digital pulses, thereby eliminating noise interference between data.
Digital switches: Schmitt Triggers can also be used as digital switches. Changing the input voltage of the trigger can cause the output level to transition from low to high or from high to low.





