Research and development in this generation is constantly evolving. The demand for power electronics, in particular, is changing dramatically. The rapidity with which technologies have impacted consumers’ habits and customs is unrivaled in the past, as they were technologically far behind. Consumers’ energy and charging habits have significantly changed in the last two or three years, and wireless technologies have fully integrated into their daily lives. Powercast helps customers to solve many remote wireless charging challenges, powering wireless sensor networks, waterproof designs, reusable smart bands, RFID tags, and many other commercial and industrial devices while launching solutions designed to power consumer electronic devices and patenting many new ideas and solutions.
Electricity is becoming increasingly important
The number of devices is undoubtedly growing. All application sectors involve the use of electronic equipment and circuits, which, of course, work with electricity. Artificial intelligence is contributing to the growth of users, and future generations will undoubtedly use technology extensively in everyday life. These devices require electricity, and the key concern is the batteries. Not only are they hefty, but they also need to be replaced on a regular basis and may possibly fail.
A green future
The need for a clean future and an unpolluted environment has become critical, and the subject has risen to the forefront of any technological conversation. The number of discarded batteries currently ending up in landfills is enormous. There are billions of them, and mines, soils, and underground aquifers are becoming increasingly contaminated. Some drastic but necessary and effective actions could include abandoning the use of batteries completely or implementing rechargeable batteries, which would prevent them from being discarded or, at the very least, ensure that they are disposed of every five or six years.
No actual energy loss
Imagine a Wi-Fi system that enables you to turn off house lights and other heavy loads when users are not physically present in a particular room. You’re making a big mistake if you focus on the simple power usage of the single device that controls and regulates the lights. So let’s take a closer look at the situation. The device in the example uses only 10 mW of power while absorbing 1 W of power from the home outlet to the wall. If we use the below formula to calculate the system’s efficiency:
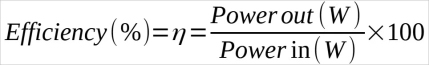
we would get an efficiency of only 1%, with a power loss of 99%. The usage of this device appears to be strongly discouraged. So if you look at the circuit from only this perspective, it’s actually quite inefficient and certainly not “green.” “Looking deeper into the true function of the charging device will reveal other wonders,” said Charles Goetz, CEO and chairman of Powercast. “The real job of the 10-mW sensor is to turn off the water heater, turn off the lights, and turn off other larger loads, and seen from this perspective, in one year, several kilowatts of electricity are being saved. Therefore, if you look at the issue from a pure physics perspective, we are actually making inefficient use of energy, but if you look at the real reason why that energy is being used and controlled, then it turns out that saving money in a year is really high and that sensor is very useful.” The transmitter in use, for example, works 24/7 and would consume a few euros in a year’s electricity bill. But these few euros make it possible to cut an annual expense of thousands of dollars if all utilities are used wisely and intelligently. There are many examples: For instance, the contactless charging of a hypothetical hand sanitizer station, otherwise powered by batteries, could be recharged at an extremely low annual cost (in the order of a few euros) using a Powercast transmitter. If adopted by a department store, the use of thousands of batteries could be avoided, resulting in saving money and reducing landfills. Another example involves charging Fluke digital multimeters (see Figure 1), one of Powercast’s most-used diagnostic tools, so that the company’s engineers can simply position and charge them automatically overnight.
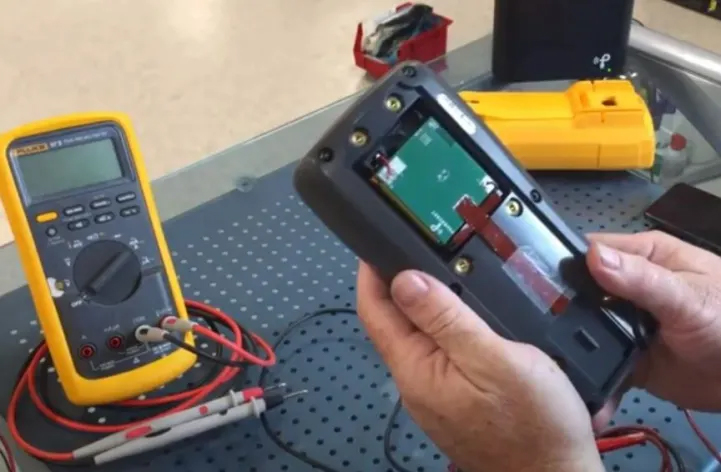

Figure 1: Fluke DMM wireless charging
A control for any type of environment
Within the sensors and transmitters, complex digital connections take place via data packets to a gateway set for a specific area. Powercast’s sensors can be used in a variety of settings, including production offices, refineries, commercial buildings, warehouses, and logistics centers. They can be placed in any position without the need for cables and, most importantly, without the need to change the batteries over time. Another interesting point is that the implementation of a new sensor does not imply a new system design but rather uses the existing RF infrastructure. This allows having a transmitter with dozens of receivers able to cover great distances. This area of technology currently poses a significant challenge to companies, as the primary goal of research is to give significantly higher power over long distances.
Powercast development tools
With Powercast development tools, you can expand the possibilities for wireless power supply. It can become a renewable energy source for rechargeable batteries and other energy storage devices. With Powercast’s patented technology, you can quickly integrate the system into any device using a plug-and-play solution for remote power. One of Powercast’s many products is the PowerSpot RF Wireless Power Development Kit for Battery Charging (P1110-EVAL-PS), shown in Figure 2. This is a complete demonstration and development platform for charging batteries in consumer devices wirelessly through RF energy (radio waves), using the PowerSpot transmitter. It is designed to be used at a higher RF power level. The recommended distance between the transmitter and the evaluation board is approximately 1.5 meters, using the PowerSpot TX91503 RF wireless transmitter. It can be used with or without its mobile app and is configured for immediate operation.

Figure 2: PowerSpot RF Wireless Power Development Kit for Battery Recharging
Another interesting kit is the Lifetime Power Energy Harvesting Development Kit for Battery Recharging (P1110-EVAL-01), shown in Figure 3. It is an all-inclusive demonstration and development platform for the development of wireless applications driven by RF energy. It is designed and configured for ultra-low power operation, and the firmware is pre-installed for immediate operation. The battery-charging boards are powered by the Powerharvester P1110 receiver, which converts RF energy into direct current. In this kit, the TX91501 transmitter or PowerSpot TX91502 (both included) act as the RF power source (915 MHz), but other 850- to 950-MHz RF sources can also be used for power. An associated app and some Bluetooth radio boards are included to quickly measure the charging current and battery voltage.

Figure 3: Lifetime Power Energy Harvesting Development Kit for Battery Recharging
Another interesting kit is the Lifetime Power Energy Harvesting Development Kit for wireless sensors (P2110-EVAL-01), shown in Figure 4. It is a complete demonstration and development platform for building wireless sensors by RF energy. It is designed and configured for very low power operation, and the firmware is pre-installed. The wireless sensor boards are powered by the Powerharvester P2110 receiver, which converts RF energy into direct current. In this kit, the TX91501 transmitter is the RF energy source (at 915 MHz), but other 850- to 950-MHz RF sources can also be used for the power supply. Communication from the sensor boards to the access point is 2.4 GHz, using 802.15.4-compliant radio signals. No batteries are required to power the wireless sensor board. On-board sensors include temperature, humidity, and light, and there is a terminal for an external sensor.

Figure 4: Lifetime Power Energy Harvesting Development Kit for Wireless Sensors
Conclusion
Powercast applies its RF wireless charging technology to real objects used every day. The RF wireless power supply applied to commonly used objects has many advantages and allows you to:
- Save time and money
- Enable new features
- Reduce battery waste and replacement costs
Powercast-powered devices include either a rechargeable battery or no battery at all, as well as the Powerharvester chip and antenna, which receives the wireless RF signal transmitted over the air by the Powercast transmitter or other RF source and converts it into usable DC energy.





