Industries with monotonous and repetitive tasks need efficiency and automation to increase output, precision, and accuracy, which resulted in a machine we all know as “a robot.” Essentially, this machine is a programmable entity that carries out automatically a complex series of actions, while its characteristics in appearance and function may differ.
From a larger perspective, robot components combine engineering, science, and technology to efficiently perform complex and monotonous tasks and produce more significant outputs. However, they are mechanically constructed and need electrical components to have power and performance. Typically, their engineering is based on the main control unit, sensors, actuation, power supply, and basic electronic parts such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits.
Jak Electronics offers a diverse selection of high-performing electrical and robot components. To experience the convenience of user-friendly online shopping, visit Jak Electronics. Let’s dig deeper to understand and analyze the functionality of electronic components in robots.
Control System
The robot’s hardware is the computation series to build a programmed central control system that asks the robot to use its components and resources to complete a particular task. System and control engineers use mathematical formulae to analyze, predict, and control a robotic system. They refine it further by using feedback loops to ensure and monitor the robotic system according to the given scenario, which cannot be left independently with the robots.
Microcontrollers and Microprocessors

The contribution of the control system is based on Microcontrollers (MCUs) and Microprocessors (MPUs). It is an integrated circuit system that may have one or more processing cores with memory and programmable peripherals. MCUs are designed to embed applications, whereas MPUs use general-purpose applications.
MCUs are used in applications needed for automatically controlled products and services. They are most commonly used in several automation industries, where embedded systems are intended for specific reasons. MCUs integrate various peripherals on a single integrated circuit, significantly different from MPUs.
Integration involves reducing size, cost, power consumption efficiency, design simplification, and reliability. The typical integration involves peripherals such as Analog Digital Converters (ADCs), Digital Analog Converters (DACs), Timers, counters, serial communication interfaces, Pulse Width Modulation Controllers, Input and output ports, comparators, memory (RAM), Real-time Operating Systems (RTOS).
Sensors
Robots identify the operating environment and understand and interpret physical occurrences into functioning electric signals. This task is completed through various sensors, including vision sensors (cameras), proximity sensors, position sensors, force sensors, and many others, to enhance the robot’s capacity to understand and learn the operating environment.
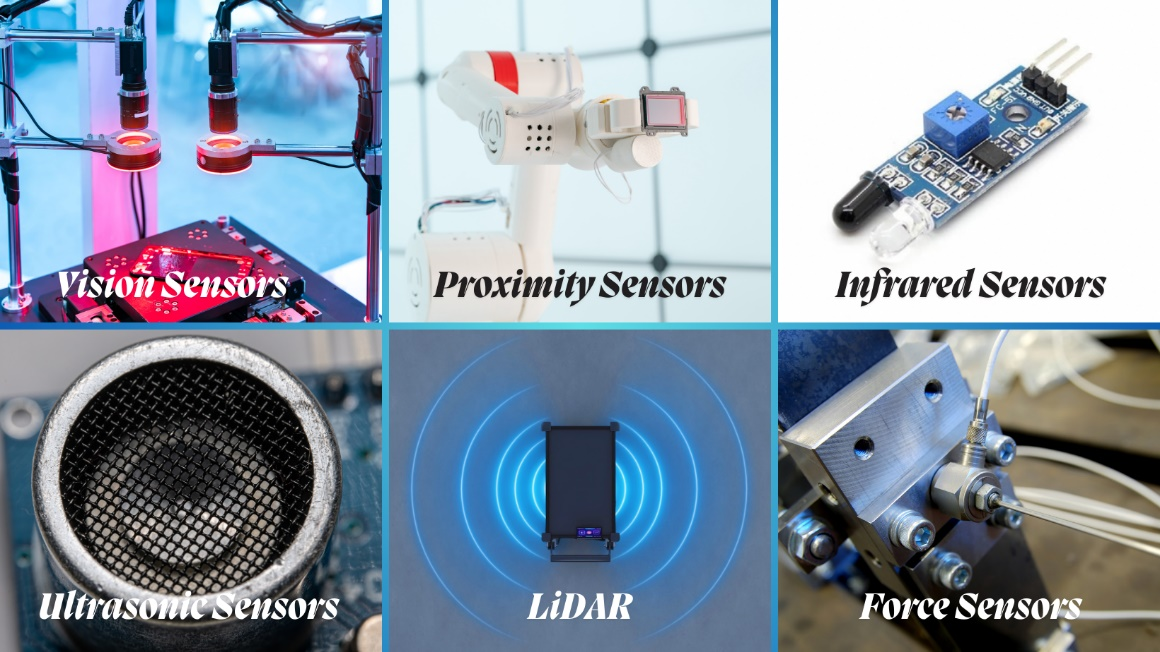

Vision Sensors
The core function is to capture, provide, and process visual information. The core electrical components include image sensors (CMOS or CCD), image processors, lenses, ADCs, and interface circuits. Image sensors are semiconductors that take images, extract light captured by the lens as electrical signals for each pixel, and operate as the robot’s electronic eyes. CMOS or CCD use photodiodes with different signal reading methods but perform similar functions to convert electronic signals into visual information.
Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors such as infrared, ultrasonic, and capacitive LiDAR are used in robots to detect object’s presence without any physical contact. The purpose of proximity sensors is to avoid, navigate, and grip objects nearby to contact. These sensors emit electromagnetic or sound waves in the field to detect objects and environmental changes.
Infrared Sensors
Infrared sensors emit infrared light to detect and measure reflected light. The intense power of infrared detects the presence of an object. The infrared sensor core components include an IR LED Emitter, a Photodiode to detect infrared light, a comparator circuit to filter out received signals, and a comparator circuit.
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sounds, and the reflected waves measure the time it takes for the sound to return. The sensor includes an ultrasonic transducer, timing circuit, signal processing circuit, and microcontroller interface.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)
LiDAR emits pulses and measures the time of reflection. These pulses measure the most accurate distances and reflect a detailed 3D imaging map. The electronic components used are a laser diode, timing circuit, photodetector, scanning mechanism, and data and signal processing units.
Position Sensors
The position sensor is used in robot manufacturing to determine the robot’s position, movement, and coordination. For this purpose, position sensors use encoders, gyroscopes, and accelerometers. The position sensors help robots move and maintain balance, navigation, and movement of the parts.
Force Sensors
Force sensors assess the force applied to a robot and are used for strain gauges to learn the deformity caused by the force applied to it. Signal refining circuits amplify and filter out signals, and converters transform analog signals into digital signals.
Other sensors include temperature, sound, tactile, pressure, laser rangefinders, GPS, contact, and environment sensors. These all function independently and provide beneficial features to robots.
Together, these sensors analyze the range, accuracy, view field, speed, environment, and density of the 3D cloud. These sensors are crucial for data processing, integration with the robot control system, frequent calibration, handling inaccurate readings, and power consumption.
Actuation And Automation

Actuators are the electronic components in robots, responsible for mechanical movement, environment interaction, and complex tasks. They turn energy into mechanical movement. Actuators are made from motors that receive signals from the control system to carry out movement patterns to complete specific tasks.
Robots have mainly two types: linear and rotary actuators. The different actuations in robots are electric, hydraulic, cable, photo-responsive, and pneumatic for process movement automation and robotic applications.
Actuators are used widely in several industries, and several factors must be considered before selecting actuators and actuation types. These factors include strength, agility, and accuracy, which lead to performance metrics. Then, the impact on robot design, compatibility, cost, safety, and potential environmental effects are considered while choosing actuators.
Power Supply

The power supply is the electrical device that powers electrical loads in robots. Robots need power to run motors, sensors, and other electrical and mechanical components. The power supply could be based on batteries, fuel cells, nuclear power, a generator, or other primary power sources. Power supply impacts robot autonomy, reliability, and performance. It is directly affected by power sources, voltage regulations, power distribution, power management, protection circuits, and their monitoring.
Communication Components
Communication is vital for robots to operate and interact with the environment, other robots, and human operators. The primary robot communication channels are wireless and wired, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Radio, Zigbee, and cellular protocols. The wired protocols include Ethernet, serial communication, and CAN. These integrated communication modules send and receive signals with the robots. The network conversation is done through point-to-point, star, and mesh network topology. The data is processed via data encoding, error detection, and security to keep the conversation private.
Other Basic Electronic Components
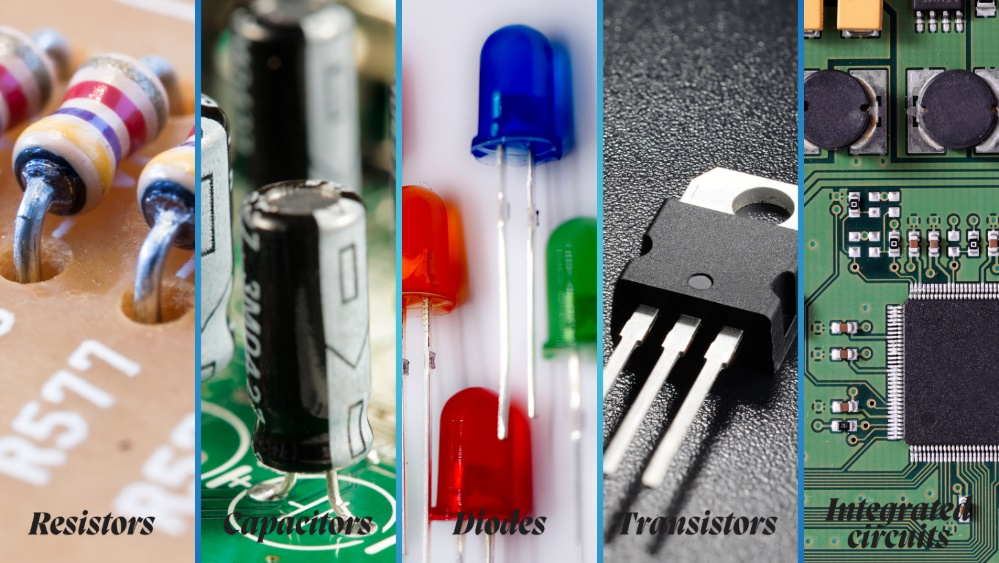
Robots also have other basic electric components, including resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits. Resistors characterize resistance value, power ratings, and temperature resistance. They limit currents to prevent damage to sensitive components. Capacitors store and release energy by filtering out voltage fluctuations, ratings, tolerance, and temperature coefficients.
Diodes protect circuits, signal rectification and routing, voltage regulation, and light emissions. The major physiognomies include forward and reverse voltage, current ratings, switching speed, and the types of diodes used. Transistors act as amplifiers and switches to process signaling, complex controlling, and power dissipation. Integrated circuits contain various resistors, transistors, capacitors, and other electrical components on a single chip to run advanced functionalities.
Conclusion
During the analytical journey of the electronic components in robots, every component plays a vital role in running robots efficiently and error-free. Any miscalculation or inappropriate use of electrical devices may result in the robot malfunctioning. Therefore, not just isolated single units but interconnected ability contributes to the overall functionality of the robots. To discover the future of electronics and empower your business, visit Jak Electronics to procure top-quality and authentic components.





