Any electronic circuit no matter the size is an assortment of components, consisting of capacitors, diode, resistors, ICs, transistors and other small devices that work together for a certain function. All these components serve a certain functionality and may as well be a critical part of the entire system. To understand any basic system, you must understand how the small components work, their function and their design.
As any system is used over a while components fail and need replacement. This happens to all systems and there are a lot of reasons why this might happen. It could be a result of power surges, manufacturing defects, normal wear and so many more.
In this article, we are going to look at ballast resistor s, what causes them to fail, the symptoms of failure and how one can test for it. But first, let us understand ballast resistors .
What is a.ballast resistor?
There are many types of resistor s. A ballast resistor in simple terms can be referred to as an electrical component that is usually used to control and limit the flow of current in a circuit, basically minimizing the risk of overcurrent fault in the circuits. Typically, electric ballasts are devices of high resistance, thus being called ballast resistors. Other devices such as capacitors, inductors or a combination can also be used as electric ballasts.
These high-resistance ballast resistors work by being placed in electrical circuits in series with the load or other electrical devices, thus effectively limiting the current that passes through them. The resistance of ballast resistors can fluctuate with the current. The resistance increases if the current passing through the resistor rises over the threshold level. Hence, when the current declines, the resistance can also do so.
The ballast resistor attempts to maintain a steady current flow across a circuit in this way. Ballast resistors can be easily confused with load resistors in that they are installed the same way. However, ballast resistors act as variable loads in a system, contrary to load resistors whose load is constant with different currents and voltages.
Nowadays, ballast resistors are rarely used in systems but are replaced by electrical circuits and ICs that can perform the same function.
In electronic circuits, a ballast resistor is often used to regulate the current flowing through a light bulb or other devices. For example, in automotive applications, ballast resistors are commonly used in the ignition system to regulate the voltage supplied to the ignition coil, which in turn controls the spark timing and combustion in the engine.
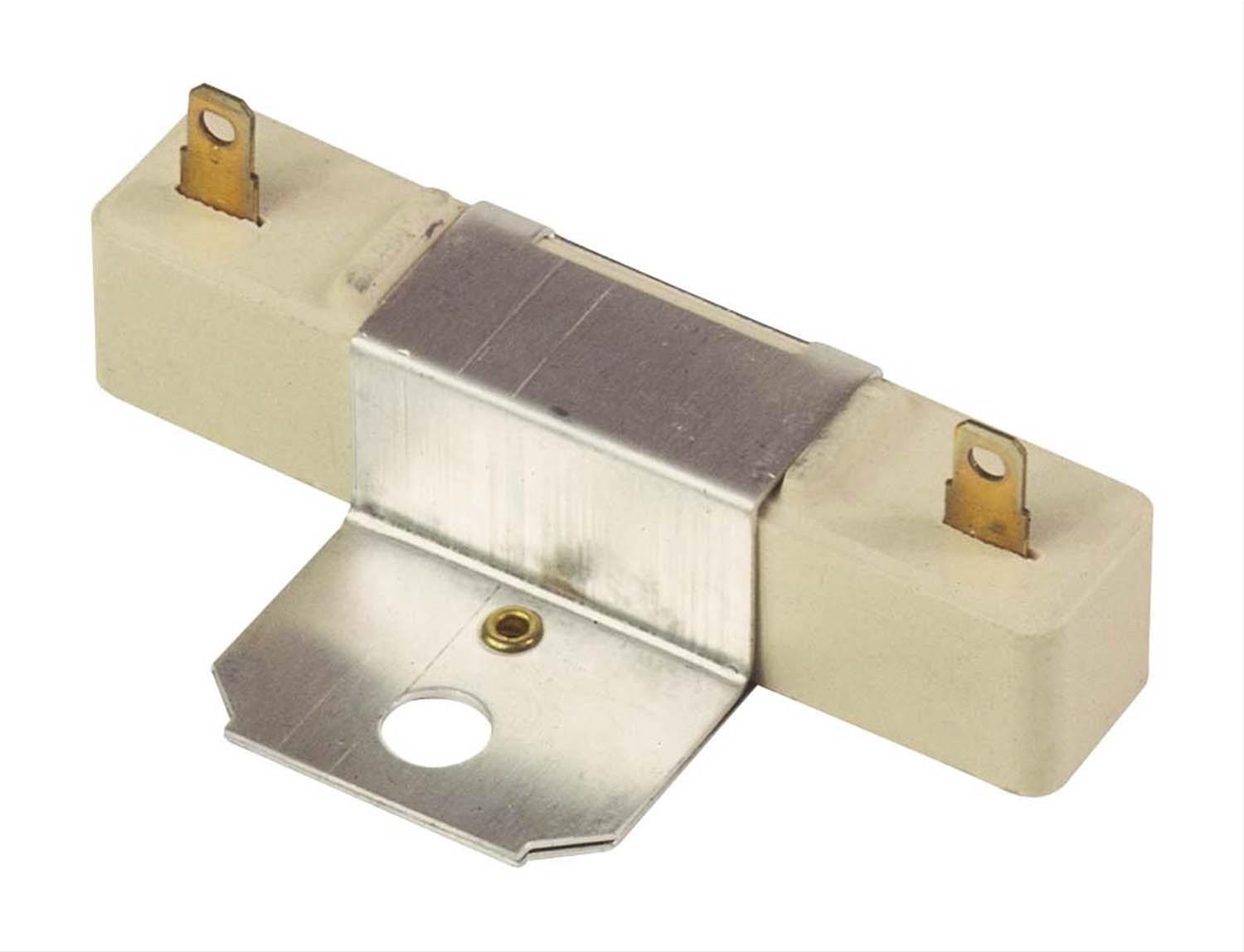
Ballast resistors can be made from various materials, such as carbon, wire wound, or metal oxide, depending on the specific application and requirements of the circuit. They are commonly rated in Ohms (Ω) and Wattage (W), indicating their resistance value and power handling capacity, respectively.
Application of a Ballast Resistor
The term “ballast” in the electrical application will often refer to stability and control. Thus, in simple terms in an application, a ballast resistor is meant to be used as a control device to help maintain stability in a system by compensating and securing other components in the circuit against changes in power input.
The voltage and current within any circuit in normal use fluctuate causing a lot of variances to make this steady, a ballast resistor is used. When used the temperature of the ballast resistor rises together with the current passing through the resistor. Moreover, as the temperature rises, the resistance does as well. As a result, a rise in resistance restricts the network's current flow.
In electronic circuits, a ballast resistor is often used to regulate the current flowing through a light bulb or other devices. For example, in automotive applications, ballast resistors are commonly used in the ignition system to regulate the voltage supplied to the ignition coil, which in turn controls the spark timing and combustion in the engine. These are also known as ignition ballast resistor s.
For this article, we are going to focus on the ballast resistors used in the ignition system of automotive. However, in an application, the tests and symptoms can be used synonymously where necessary.
How it works
Ballast resistors are used in automotive ignition systems to limit the current flowing through the ignition coil. The primary purpose of the ballast resistor is to prevent the ignition coil from overheating and to extend its lifespan.

When the ignition key is turned on, current flows from the battery to the ignition coil. The ignition coil then steps up the voltage and sends it to the distributor, which in turn sends the voltage to the spark plugs. However, if the ignition coil is left on for an extended period, it can overheat and be damaged.
To prevent this, a ballast resistor is used to limit the current flowing through the ignition coil. The ballast resistor is placed in the circuit between the ignition switch and the positive terminal of the ignition coil. The resistor has a high resistance, which limits the amount of current flowing through the circuit.
Since the ignition system needs a lot of power, thus high voltage equal to the supply at the initial start, a jumper cable is normally connected with the ballast resistor. This allows for the ballast resistor to be bypassed, allowing full battery voltage to reach the ignition coil when the engine is started. This provides a strong spark for starting the engine. Once the engine is running, the ballast resistor is switched back into the circuit, reducing the voltage to the ignition coil and limiting the current flow.
Symptoms of a Faulty Ballast Resistor
It is important to note that most modern vehicles may not have ballast resistors but in turn, are fitted with more advanced control circuit boards. Only older vehicles have a likelihood of having ballast resistors.
Over time and long periods of use, ballast resistors incur failure either from normal wear, faulty batteries or other failing components of the system. If the ballast resistor in an automotive ignition system is faulty, it can lead to several symptoms that can affect the performance of the vehicle.
When you suspect a faulty or failing ballast resistor, here are a few things that you should look out for:
- Hard Starting the Engine
One of the most obvious and common signs of a failing ballast resister will be a failed start. The vehicle starts and immediately dies when the key is released, especially when the engine is cold. This is because the resistor may not be allowing enough voltage to reach the ignition coil, leading to a weak spark and difficulty in starting the engine.
This fault can easily be diagnosed by having the voltage across the coil measured during and after ignition.
- Rapid Misfire / Rough Idling
A rough idling or a misfire is the excessive shaking or vibrations experienced in an idling engine. A faulty ballast resistor can cause misfiring or rough idling. This is because the resistor may not be allowing enough voltage to reach the ignition coil, leading to a weak spark and incomplete combustion. This happens as the spark plugs do not receive enough power for proper firing causing random misfires during the sparking process.
- Stalling
Stalling is normally a sign of poor or faulty engine operation. It can be caused by several things, one of which is a bad ballast resistor. A faulty ballast resistor can also cause the engine to stall or shut off completely. This is because the resistor may not be allowing enough voltage to reach the ignition coil, leading to a weak spark and complete loss of power.
- Overheating
As earlier stated, when too much current is exerted into a system, the overall response is overheating. If the operation of the ballast resistor is faulty and is not controlled this is transferred to the rest of the system. The faulty ballast resistor can cause the ignition coil to overheat, leading to premature failure. This can be due to the resistor not providing enough resistance to limit the current flow, causing the ignition coil to work harder than it should.
How to test a ballast resistor
The ballast resistor is used to regulate the voltage levels of the ignition coil, thus there are two ways of testing for the proper function of this resistor. One is by establishing the resistance range as specified and the other is by measuring the output voltage. To be able to measure this, you will need an ohmmeter and a multimeter.
The battery is typically utilized to power the ignition system. Moreover, the battery voltage is often 12V or 24V. We must decrease the voltage to lengthen the ignition coil's lifespan. and a ballast resistor is connected to the ignition coil to achieve this goal.
So, we may measure the voltage across the ignition coil to evaluate the ballast resistor. If the voltage level is within 7-8V, the ballast resistor is functioning properly. A high voltage level would indicate a failed ballast resistor.
Here are the steps to electronics.com/productdetail/sgmicro-sgm809xxn3tr-20982402">www.jakelectronics.com/blog/what-is-resistor-and-its-function">jakelectronics.com/blog/symptoms-of-a-bad-ballast-resistor-and-how-to-test-it">test a ballast resistor:
- Locate the ballast resistor in the ignition system. It is usually located near the ignition coil or the distributor.
- Disconnect the wire connector from the ballast resistor.
- Set your multimeter to the resistance (ohms) setting.
- Place one probe of the multimeter on one of the terminals of the ballast resistor and the other probe on the other terminal.
- Check the resistance reading on the multimeter. The resistance value should be within the specified range for your specific vehicle make and model. You can refer to the vehicle's service manual for the correct resistance value.
- If the resistance value is not within the specified range, the ballast resistor may be faulty and needs to be replaced.
- To check if the ballast resistor is allowing enough voltage to reach the ignition coil, connect the wire connector back to the ballast resistor.
- Set your multimeter to the voltage (volts) setting.
- Turn on the ignition switch and measure the voltage across the positive and negative terminals of the ignition coil. The voltage reading should be within the specified range for your specific vehicle make and model.
- If the voltage reading is not within the specified range, the ballast resistor may be faulty and needs to be replaced.
As some models have a bypass connected with the ballast resistor, this would require the help of a manual in order to disconnect the bypass during testing. Otherwise, you might get false results.
Lastly
Overall, the ballast resistor is an important component of the automotive ignition system that helps to protect the ignition coil from overheating and extends its lifespan.
Although it is important to understand how your car works and the common diagnosis of common faults, it is imperative that you have your system inspected, serviced and repaired by a qualified mechanic to determine the fault and the cause of the fault. In this case, if the ballast resistor is the cause of the problem.






