A voltage follower is a circuit that produces an output voltage that closely follows the changes in the input voltage. It finds widespread application in electronic devices, particularly in signal amplification and control circuits. In this article, we will explore the definition, working principle, and applications of a voltage follower.
What is a Voltage Follower?
A voltage follower is an amplification circuit in which the output voltage is the same as the input voltage.
This circuit has a high input impedance, low output impedance, and a voltage gain of 1. This means that the voltage follower has minimal impact on the input voltage signal, and the output voltage is equal to the input voltage. The output current can be relatively large. The following diagram shows a voltage follower implemented using an operational amplifier (op-amp).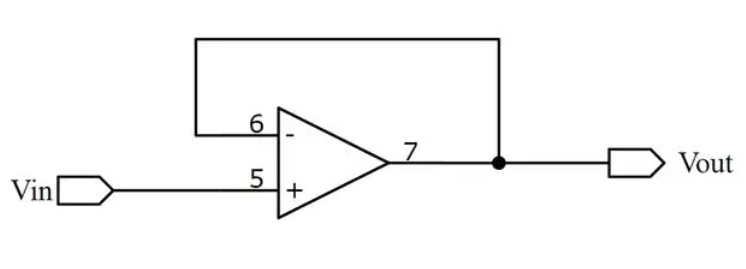
Fig 1: A voltage follower built with an op amp
How does a Voltage follower work?
A voltage follower is a feedback circuit that utilizes negative feedback to achieve matching between the output voltage and the input voltage. It consists of two fundamental components: an amplifier and a feedback circuit. The amplifier can be of any type, such as a common emitter amplifier, common base amplifier, or common collector amplifier. The role of the feedback circuit is to compare the output signal of the amplifier with the input signal and feed back the difference to the input of the amplifier to maintain the stability of the output voltage.
Here is a typical circuit diagram of a voltage follower:

Fig 2: Typical circuit diagram of a voltage follower
ALSO READ: Understanding Operational Amplifiers: A Comprehensive Guide
What does the voltage follower do?
An operational amplifier circuit is a circuit with very high input impedance, and this high input impedance is the reason for using a voltage follower. The following is a summary of the role of a voltage follower.
1.Voltage Follower consumes very little current.
When a circuit has a very high input impedance, it draws very little current from the circuit. According to Ohm's law, current I = V/R. Therefore, the higher the resistance, the less current is drawn from the power source.
As a result, when current is fed into a high impedance load, the power of the circuit is not affected.
Let's look at the two following circuit diagram.

Fig 3: The circuit that Power supply supplies power to a low-impedance load
In this circuit above, the load requires and consumes a lot of current because the load is low impedance. According to Ohm's law, the current I=V/R. If the resistance of the load is very low, it will consume a lot of current. This results in a large amount of power being drawn from the power supply, and consequently leads to high interference and the use of the power supply powering the load.
Now let's look at the following circuit, connected to the op amp voltage follower:
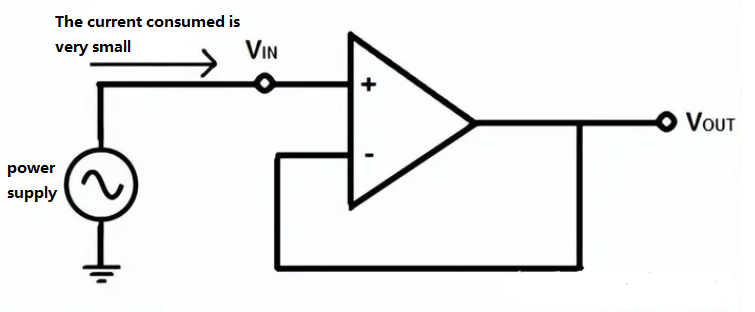
Fig 4: voltage follower circuit
The top circuit now draws very little current from the top power supply. Because the operational amplifier has such a high impedance, it consumes very little current. And because an op amp without a feedback resistor provides the same output, the circuit outputs the same signal as the one fed in.
This is also one of the reasons for using a voltage follower, which consumes very little current, does not interfere with the original circuit, and provides the same voltage signal as the output.
The voltage follower acts as an isolation buffer, isolating the circuit so that the circuit's power supply is subject to very little interference.
2、Voltage follower is important in voltage divider circuit
In voltage divider circuits, a voltage follower can be used to mitigate the loading effect caused by the load connected to the output of the voltage divider. A voltage divider is a simple circuit arrangement consisting of two resistors connected in series, typically used to obtain a fraction of the input voltage at the output.
However, when a load is connected to the output of the voltage divider, it can introduce an additional load resistance and affect the output voltage. This loading effect can cause a deviation from the desired output voltage and impact the accuracy of the voltage division.
To overcome this issue, a voltage follower can be incorporated into the voltage divider circuit. The voltage follower is connected between the output of the voltage divider and the load.
In this configuration, Vin represents the input voltage, Vout is the output voltage of the voltage divider, and the Load represents the connected load. The voltage follower, implemented using an operational amplifier, is connected between Vout and the Load.
The voltage follower acts as a buffer between the voltage divider and the load, isolating the load from the voltage divider circuit. It presents a high input impedance to the voltage divider, ensuring minimal loading effect. Simultaneously, it provides a low output impedance, allowing it to drive the load effectively.
By using a voltage follower in a voltage divider circuit, the output voltage remains stable, and the accuracy of the voltage division is maintained even when a load is connected. The voltage follower minimizes the impact of the load resistance on the output voltage, ensuring that the load receives the intended voltage level without significant deviation.
Overall, the inclusion of a voltage follower in voltage divider circuits helps address the loading effect and enhances the performance and accuracy of the voltage division, particularly when driving loads with varying impedance.
ALSO READ: Current Divider: definition, applications & formula
Applications of Voltage Followers
Voltage follower is widely used in electronic equipment, its main role is to maintain the stability of the signal and amplify the signal. Here are the main applications:
- Signal amplifier
The voltage follower can act as a signal amplifier, amplifying the input signal for further processing. For example, it can be used in audio amplifiers, video amplifiers, and circuit controllers.
- Voltage regulator
The voltage follower can be used as a voltage regulator to maintain the stability of the output voltage. For example, it can be used for DC power supplies, battery chargers and LED drivers.
- Signal buffer
The voltage follower can be used as a signal buffer to avoid signal loss and distortion. For example, it can be used for sensor signal amplification and signal line drivers.
- Industrial controller
Voltage follower can be used in industrial controllers to maintain the stability of the output signal and control the operation of industrial equipment. For example, it can be used in aspects such as PLC (programmable logic controller) and PID (proportional integral differential) controller.
Advantages of Voltage Followers
Provides a gain in power and current
The output impedance of the circuit is small and the output is used
The op amp uses zero current from i/p.
The loading effect is avoided.
Does not increase or decrease the amplitude of the input signal
High-frequency noise cannot be filtered out
Has a small output impedance
High input impedance
Unit transmission gain
Why use a voltage follower?
There are several important reasons to use a Voltage Follower:
- Impedance matching: Voltage follower has the characteristics of high input impedance and low output impedance. It can effectively match the impedance of the input source to the impedance of the subsequent circuit or load. This helps reduce impedance mismatches between the signal source and the back-end circuit, ensuring high-quality signal delivery and minimal signal distortion.
- Signal buffer: The voltage follower can provide the function of signal buffer. When the impedance of the input signal source is high, the use of a voltage follower can prevent the signal source from being affected by the impedance of the load circuit. It can withstand the current demand of the load, maintain the stability of the input signal, and pass the signal to the subsequent circuit or device.
- Circuit isolation: The voltage follower can achieve the effect of circuit isolation. By isolating the input signal source from the subsequent circuit, the voltage follower prevents interference or noise from the signal source from propagating into the subsequent circuit. This is very important to maintain the purity of the signal, reduce interference and improve the anti-interference ability of the system.
- Signal amplification and transmission: Although the voltage gain of the voltage follower is 1, that is, it does not provide any amplification, it can accurately transmit the characteristics of the input signal to the subsequent circuit or load. It can provide stable signal magnification and maintain the accuracy and stability of the input signal to meet the needs of specific applications.
- Stability and accuracy: The use of voltage follower can improve the stability and accuracy of the circuit. It can offset the influence of impedance changes, temperature changes or load changes of the input signal source on the output signal. By providing a stable output voltage, the voltage follower helps maintain the accuracy and reliability of the system.
To sum up, the voltage follower has a wide range of applications in circuit design. It can solve the problems of impedance matching, signal buffering, circuit isolation, stability and accuracy, so as to improve the performance of the circuit and signal quality, and ensure the reliable transmission and accuracy of the signal.






