Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) has disrupted the interaction between devices, the physical world, and the cloud. IoT applications can be found in smart homes and wearable devices, as well as industry automation and smart cities. The core of any IoT system is a microcontroller, which performs data processing, communication, interfaces with sensors, and manages power. A microcontroller is not a small thing to consider. It has a direct impact on the performance of your project, power efficiency, scalability, development time, and cost. Some of the successful alternative incorporators nowadays have included Arduino, ESP32, and STM32.
JAK Electronics offers high-performance microcontrollers and essential IoT components that power smart devices and scalable systems. Discover multiple options by clicking here.
Understanding Microcontrollers in IoT
A microcontroller is a small integrated circuit that houses:
· A processor (CPU)
· Memory (RAM and Flash)
· Input/output peripherals
· Communication interfaces
In IoT systems, microcontrollers perform tasks such as:
· Reading data from sensors
· Processing and filtering information
· Communicating via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or wired protocols
· Managing power consumption
· Executing control logic
When selecting a microcontroller for IoT, engineers typically evaluate:
· Processing power
· Memory capacity
· Connectivity
· Power efficiency
· Development tools
· Community and ecosystem
· Cost and scalability
Let’s analyze Arduino, ESP32, and STM32 in detail.
Overview of Arduino
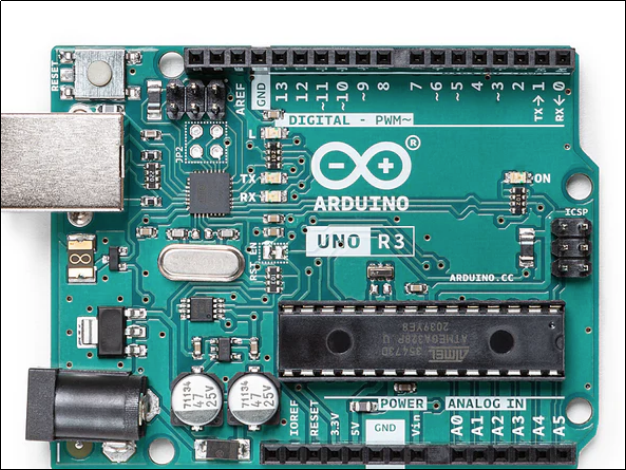
Arduino is one of the most popular embedded industry platforms. Arduino is not a single chip, it is an environmental system that contains development boards, an easy-to-use IDE, and a large collection of libraries.
The 8-bit AVR microcontrollers, including the ATmega328P, are the basis of most Arduino boards.
The known Arduino boards include:
· Arduino Uno
· Arduino Nano
Hardware Capabilities
Arduino boards are normally 16 MHz and have limited memory:
· Flash: 32 KB
· SRAM: 2 KB
· EEPROM: 1 KB
The standards are adequate in simple applications but restrictive to more complex IoT applications such as networking, encryption, or multi-tasking.
Wi-Fi or Bluetooth is not built into any Arduino boards. Wi-Fi shields, such as external shields (ESP8266, Wi-Fi shields), are needed, and these add complexity to the system.
Development Environment
The best feature of Arduino is its simplicity. The Arduino IDE:
· Uses simplified C/C
· Minimal configuration is required.
· Incorporates thousands of libraries.
· Allows fast prototyping
Novices are able to get started on functional projects in a matter of hours.
Power Consumption
Arduino is not optimized for extremely low power. Although there are power-saving methods, the majority of the boards use a lot of energy to run long-term battery-saving IoT devices.
Ideal Use Cases
Arduino is best suited for:
● Learning embedded systems
● Educational projects
● Rapid prototyping
● Basic automation systems
● Simple jakelectronics.com/productdetail/feigelectronic-360500000-1770567">electronics.com/">jakelectronics.com/productdetail/sgmicro-sgm809xxn3tr-20982402">www.jakelectronics.com/solution/signs-of-a-bad-camshaft-position-sensor-and-how-to-test-it">sensor applications
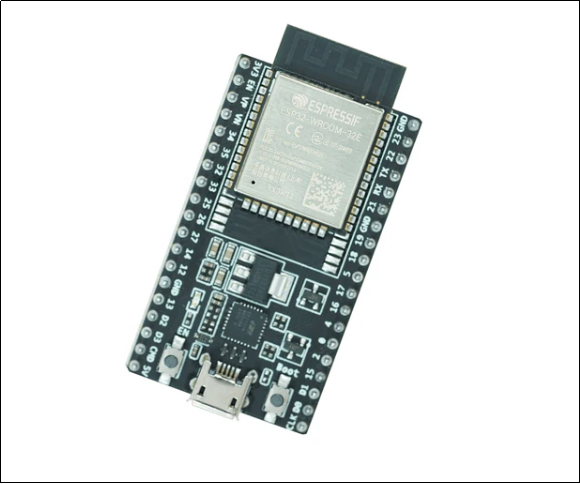
Overview of ESP32
ESP32 by Espressif Systems is among the strongest and inexpensive microcontrollers to use in IoT. It was tailored to both interconnected devices and Web 2.0.
ESP32 also includes Wi-Fi and Bluetooth on-chip, as opposed to Arduino.
Hardware Capabilities
● Dual-core 32-bit CPU
● Clock speed up to 240 MHz
● Hundreds of KB of SRAM
● External Flash support
Built-in features include
● Wi-Fi (802.11 b/g/n)
● Bluetooth Classic & BLE
● ADC, DAC
● Touch sensors
● SPI, I2C, UART
● Secure boot and hardware encryption
Development Environment
ESP32 is compatible with several development environments:
● Arduino IDE (new, user-friendly)
● ESP-IDF (professional-grade)
● PlatformIO
Power Efficiency
ESP32 has advanced power modes:
● Deep sleep
● Light sleep
● Dynamic frequency scaling
Ideal Use Cases
● Smart home devices
● IoT dashboards
● Wireless sensor networks
● Wearables
● Cloud-connected systems
Overview of STM32
STMicroelectronics designs STM32 microcontrollers that are extensively deployed in industrial, automotive, and commercial applications. They are founded on ARM Cortex-M cores.
The STM32 family includes:
● STM32F (general purpose)
● STM32L (low power)
● STM32H (high performance)
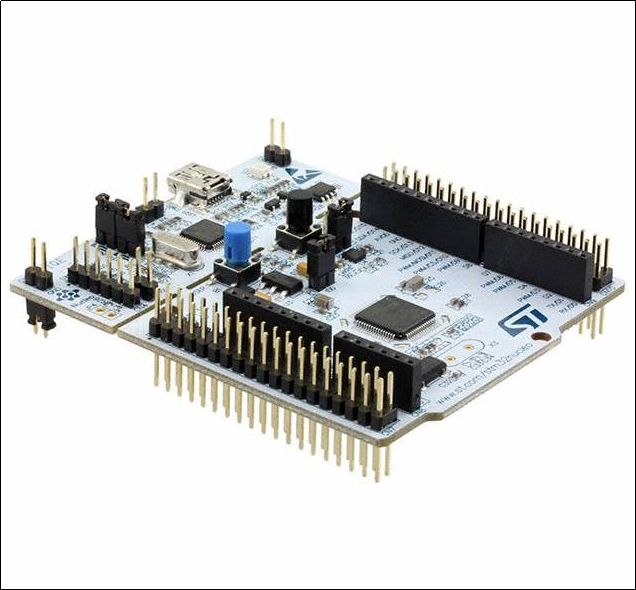

Hardware Capabilities
● Clock rates of hundreds of MHz
● Large Flash and SRAM options
● Advanced peripherals
● Real-time performance
● Precise timing
● Motor control
● Signal processing
Development Environment
The development of STM32 is more difficult, yet more powerful:
● STM32CubeIDE
● Keil MDK
● IAR Embedded Workbench
STM32CubeMX makes it easier to configure the peripherals, but it needs more embedded skills.
Power Consumption
STM32 has been associated with very-low-power development, particularly the STM32L series. When used in applications that sleep a lot, these chips run on a single battery for years.
Ideal Use Cases
● Industrial IoT
● Medical devices
● Automotive electronics
● Real-time control systems
● Embedded products are used commercially.
Comparison Summary
|
Feature |
Arduino |
ESP32 |
STM32 |
|
Performance |
Low |
High |
Very High |
|
Built-in Connectivity |
No |
Yes |
Usually No |
|
Ease of Use |
Very Easy |
Moderate |
Advanced |
|
Power Efficiency |
Low |
Good |
Excellent |
|
Scalability |
Limited |
High |
Very High |
|
Professional Use |
Limited |
Moderate |
Extensive |
Which Microcontroller is the one to use?
Choosing the appropriate microcontroller is chosen according to the level of experience, level of project, connection capabilities, power considerations, and long-term objectives. In this manner, both platforms are well-suited to particular tasks, and their differences will guide you in not over-engineering or under-powering your IoT.
Choose Arduino if:
1. You are a beginner or student.
Arduino is aimed at students who have limited or no experience in embedded systems. It is easy to program, requires a large learning community, and is ideal to learn the basics of microcontrollers and electronics.
2. You desire learning fast and prototyping.
Arduino enables you to transform ideas into working prototypes in a very short time due to little setup, plug-and-play hardware, and thousands of available, ready-to-use libraries.
3. Your project is amateur, non-commercial, or academic.
Arduino is very apt in simple sensor reading, LEDs, small-scale automation, or proof of concept, where high-performance and wireless accessibility are not vital.
4. Support in the community is more important than optimization.
The Arduino ecosystem provides very long tutorials, forums, and open-source examples, thus saving a lot of time on simple project development.
Choose ESP32 if:
1. Your project must have built-in Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
ESP32 is designed specifically to serve the IoT applications, providing onboard wireless connectivity without having to add any external modules.
2. You are constructing intelligent or networked equipment.
It can be used in smart homes, remote monitoring, cloud-connected sensors, and wearable devices that are designed to be connected to the internet or mobile networks.
3. desire performance at a cheap cost
ESP32 offers unprecedented value alongside money due to its powerful, dual-core processor, large memory, and integrated security features, among other things, compared to most of the substitutes.
4. You should strike a balance between convenience and functionality.
ESP32 is compatible with Arduino and other introductory programmable development platforms, as well as the ESP-IDF high-level development platform, thus it is adaptable to hobby projects, launched to large IoT products.
Choose STM32 if:
1. You are creating a business or professional product.
STM32 microcontrollers dominate the industrial, medical, and automotive sectors, where stability and durability in the market are paramount.
2. You simply cannot get away with anything but real-time, precise, and deterministic control.
STM32 is optimally used in motor control, signal processing, and control systems with its high level of timers, DMA, and real-time processors.
3. Critical parameters are power efficiency and reliability.
STM32 supports long-battery-life variants, which are ultra-low-power, that are used to make them useful in energy-sensitive IoT applications.
4. You require customization and scalability.
The STM32 family offers many options in the level of performance and peripherals to facilitate designs that can be both low-end and high-end systems without altering the architecture.
Conclusion
Arduino, ESP32, and STM32, as opposed to each other, have other purposes in the embedded and IoT ecosystem. Arduino prioritizes simplicity and learning, ESP32 is billed as a strong wireless IoT connection with very high performance and low costs, and STM32 is said to be industrial grade as far as reliability, accuracy, and scalability are concerned. The best option depends on the needs of your project and your technical skills, and your long-term goals. The right microcontroller in the first place will offer an efficient development, stable performance, and a flexible base on which to build the upper limit of your IoT project.
To explore the right development solution for your next IoT project and power your ideas with Arduino, ESP32, or STM32, visit JAK Electronics.






